Vol. 14, No. 10 / Economic Impacts of Mississippi Saltwater Recreational Fishing Industry
ABSTRACT
- This newsletter summarizes the economic impacts of the Mississippi saltwater recreational fishing industry from 2014 to 2022.
- The economic impact indicators include income, value-added, output or sales, and employment or job impacts.
- The saltwater recreational fishing industry components included in this presentation are charter boats for hire, private boats fishing, and shore fishing.
- The fishing-related durable expenditures are excluded due to the lack of data starting in 2019.
- The losses to the industry associated with the Bonnet Carre Spillway disaster in 2019 and the COVID-19 pandemic starting in 2020 are measured.
KEYWORDS
Economic impacts, Mississippi saltwater recreational fishing, charter boats for hire, private boats, shore fishing.
METHODS
- The losses to the industry associated with the Bonnet Carre Spillway disaster in 2019 and the COVID-19 pandemic starting in 2020 are estimated using the Mean-Difference model.
- The Mean-Difference model estimates losses associated with a major disaster by comparing the values of selected economic indicators during the year the disaster occurred to their means during the benchmark period.
- The benchmark period is the years immediately preceding the year the disaster occurred. It is preferred to be at least three consecutive years without any other major disaster.
- Losses occur when the current values are less than the benchmark means.
COMPONENTS OF ECONOMIC IMPACTS (IMPLAN, 2024)
- The total economic impact is the sum of direct, indirect, and induced impacts.
- Direct impacts express the economic impacts in the sector where the expenditure was initially made.
- Indirect impacts result from changes in the economic activity of other industrial sectors that supply goods or services to the sector being evaluated.
- Induced impacts are the result of personal consumption expenditures by industry employees.
TYPES OF ECONOMIC IMPACTS (IMPLAN, 2024)
- Four economic impacts include output or sales, jobs, income, and value-added. These impacts are not additive. Each type represents a specific economic activity reported.
- Output or sales are the gross sales by businesses within the economic region affected by an activity.
- Labor income includes personal income such as wages and salaries and proprietors' income or income from self-employment. Labor income consists of all forms of employment income, including employee compensation -- wages, salaries, and benefit and proprietor income.
- Value-added impacts measure an industry's addition to the gross domestic product. It is the difference between an Industry's total output and the costs of its intermediate inputs.
- Income, value-added, and output impacts are expressed in dollars for the year specified by the user.
- Employment impacts are expressed in terms of a mix of both full-time and part-time jobs.
SOURCES OF DATA
- Estimates of the economic impacts of the seafood industry were compiled from the Fisheries Economics of the United States Reports prepared by NOAA Fisheries.
- https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/resource/document/fisheries-economics-united-states-report.
COMPONENTS OF THE MISSISSIPPI SALTWATER RECREATIONAL FISHING INDUSTRY
- Charter boats for-hire
- Private boat fishing
- Shore fishing
- Fishing-related durable expenditures
MISSISSIPPI MARINAS
- An online list of Mississippi marinas that have fully functioning pump-out or dump stations for proper disposal of all vessel wasters is posted on the Mississippi Department of Marine Resources website.
MISSISSIPPI MARKETMAKER
- An online directory of registered recreational fishing businesses is available on the Mississippi MarketMaker website.
- An online list of recreational fishing businesses is shown when you type "fishing charter" in the search box.
TOTAL MISSISSIPPI SALTWATER RECREATIONAL FISHING TRIPS
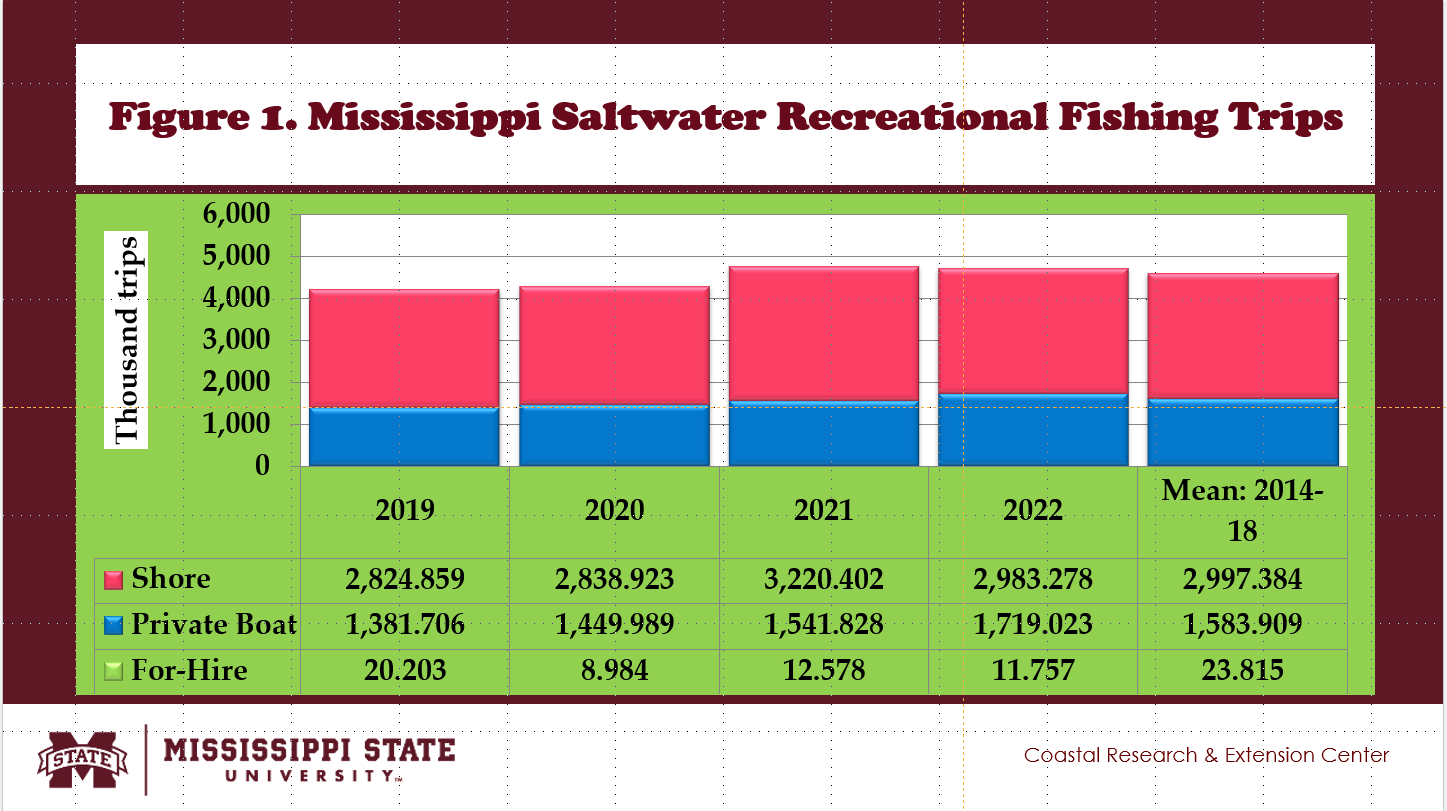
- Fig. 1 shows the annual estimates of the number of fishing trips made in the three modes of saltwater sport fishing in Mississippi
- Compared to the mean values between 2014 and 2018, the total number of saltwater recreational fishing trips was lesser in 2019 and 2020.
- An average of 4.61 million fishing trips were recorded from 2014 to 2018.
- The total number fell to 4.23 million fishing trips in 2019 and 4.29 million in 2020.
- The total number of fishing trips rose to 4.77 million in 2021 and 4.71 million in 2022.
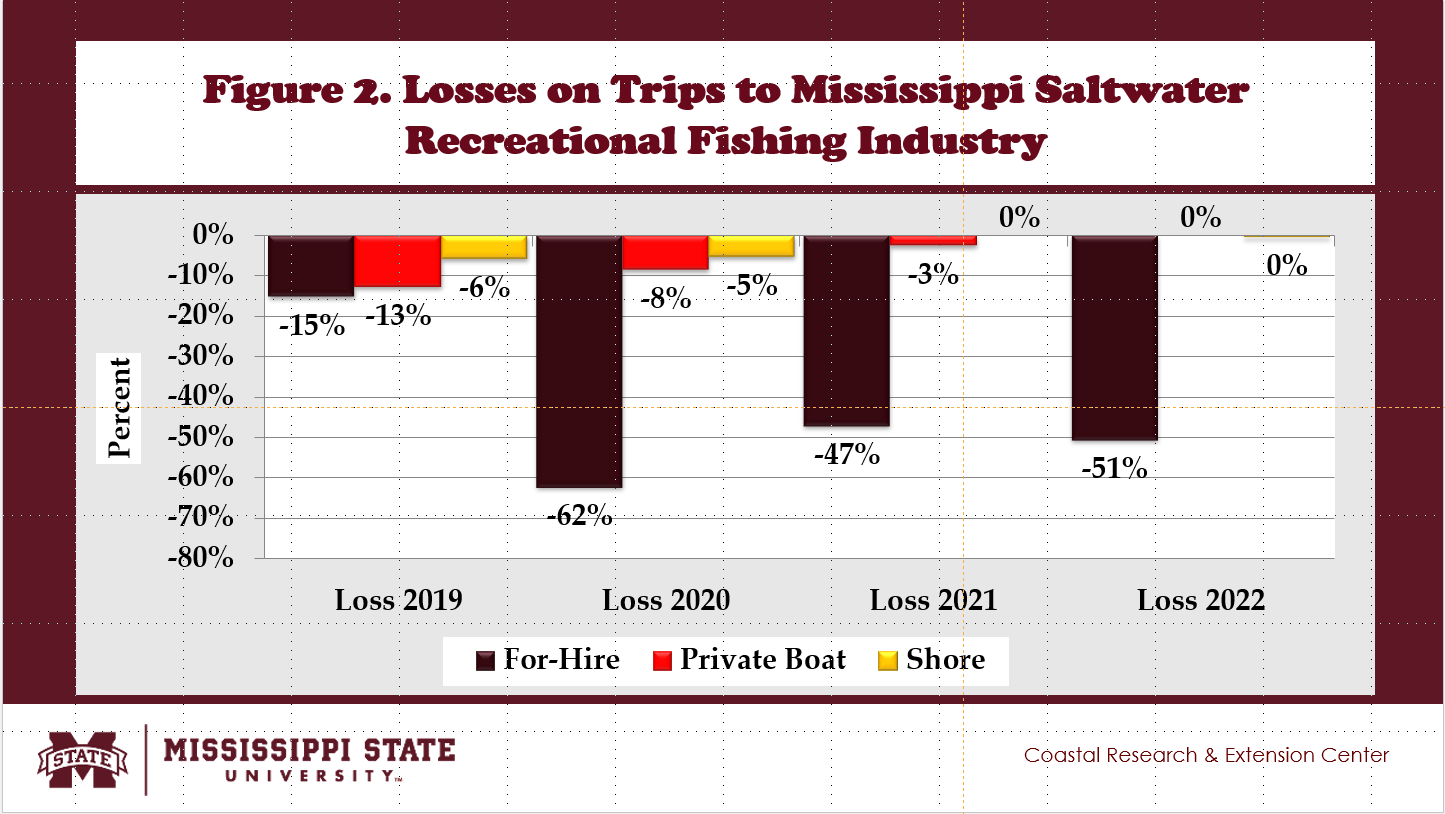
- Total Mississippi saltwater fishing trips decreased by 8% and 7% in 2019 and 2020. No losses in total fishing trips were observed in 2021 and 2022.
- The number of trips made by Mississippi charter boats for hire fell about 15%, 62%, 47%, and 51% in 2019, 2020, 2021, and 2022, respectively.
- The Mississippi private boat saltwater fishing trips decreased by about 13%, 8%, and 3% in 2019, 2020 and 2021, respectively.
- The Mississippi saltwater shore fishing trips decreased by 6% and 5% in 2019 and 2020.
ECONOMIC IMPACTS OF MISSISSIPPI SALTWATER RECREATIONAL FISHING
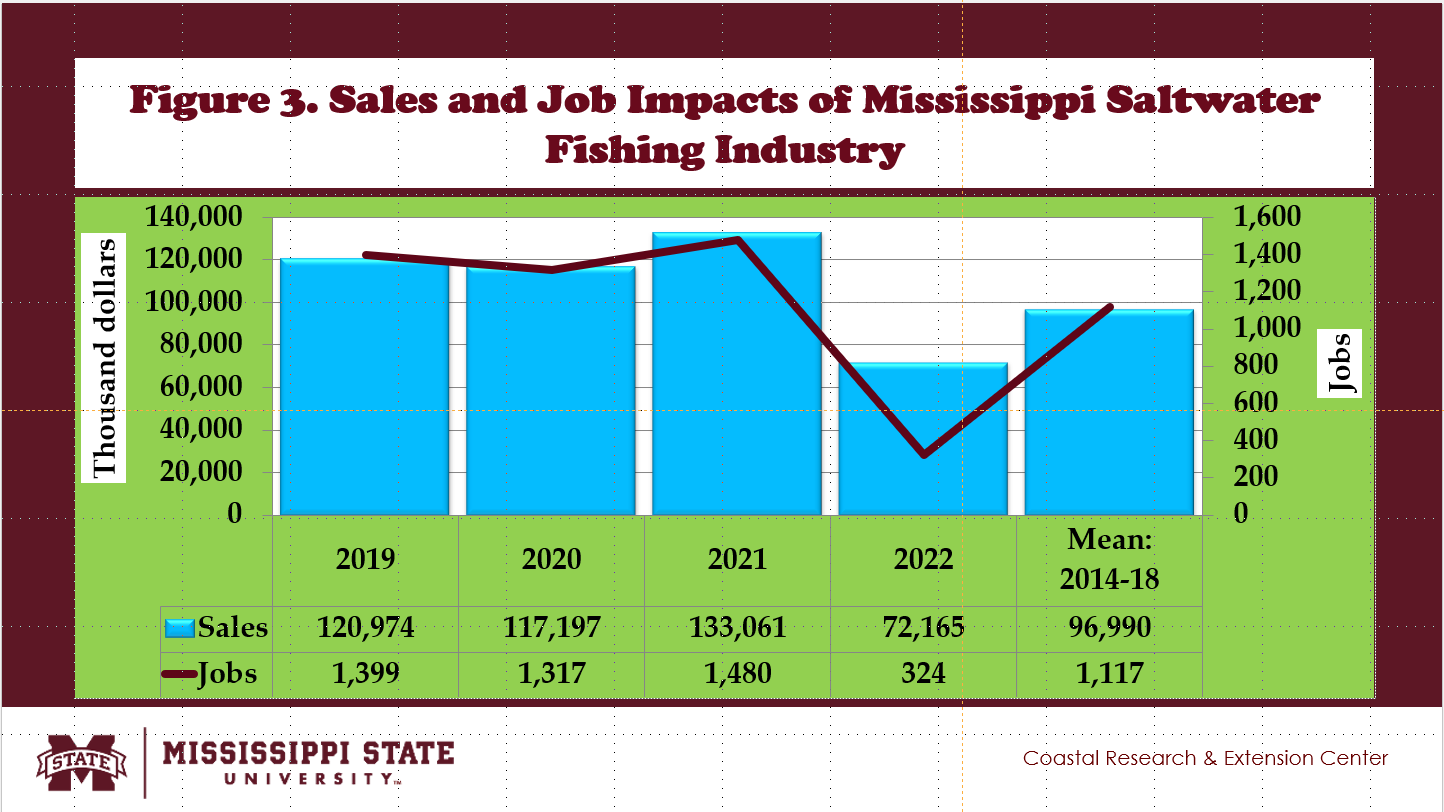
- Fig. 3 shows the annual estimates of the total economic impacts of the Mississippi saltwater recreational fishing industry from 2014 to 2022.
- Between 2014 and 2018, the benchmark mean of total sales impacts reached $96.99 million, contributing 0.5% of the U.S. saltwater recreational fishing industry.
- A total of 1,117 jobs were created in Mississippi by the saltwater recreational fishing industry, adding 1.0% to the U.S. saltwater recreational fishing industry (Fig. 3).
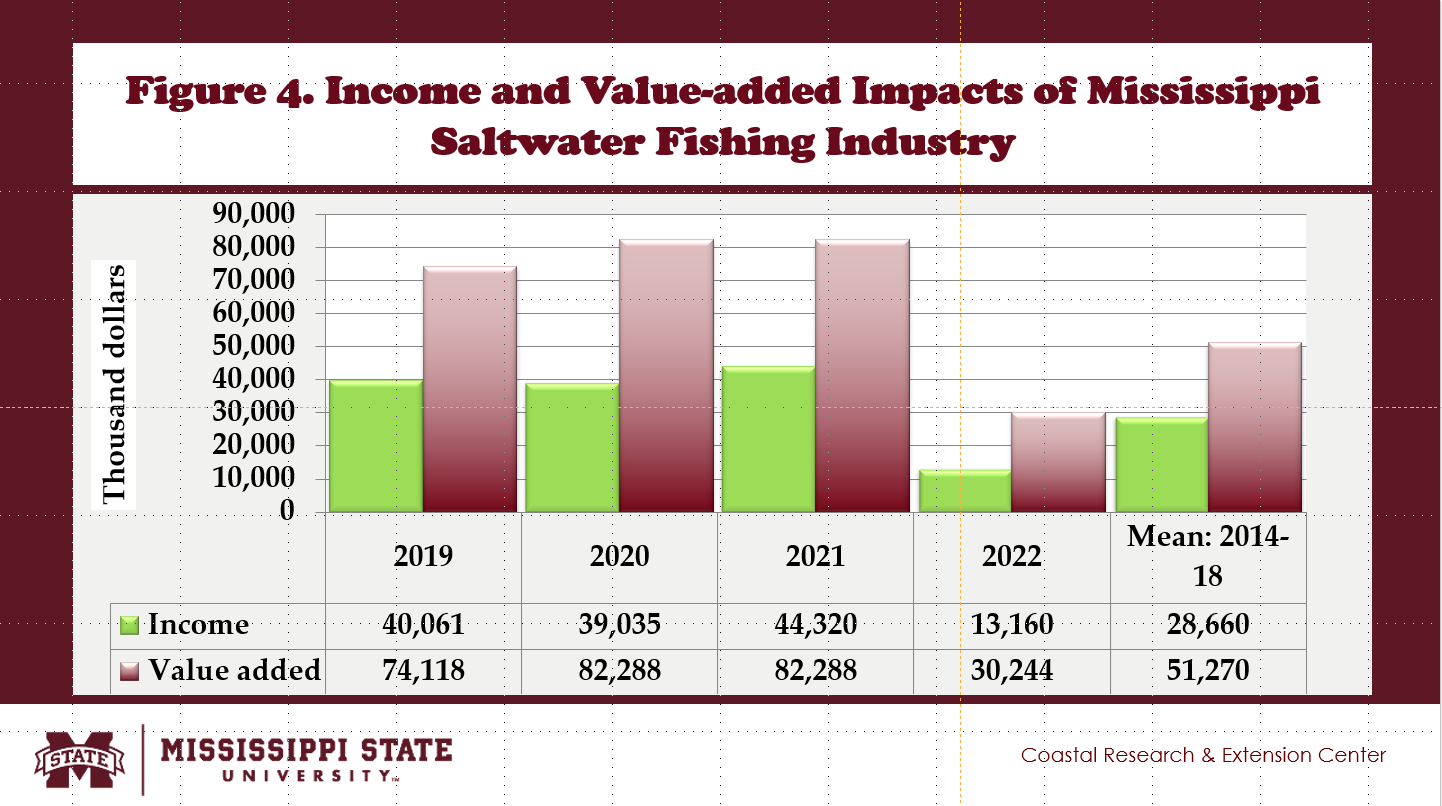
- The saltwater recreational fishing industry in Mississippi generated total income impacts of $28.66 million, adding 0.6% to the U.S. saltwater recreational fishing industry (Fig. 4).
- Total value-added impacts created by the saltwater recreational fishing industry in Mississippi averaged $51.27 million, contributing 0.6% of the U.S. saltwater recreational fishing industry (Fig. 4).
MISSISSIPPI CHARTER BOATS FOR-HIRE FISHING
- Compared to the mean values between 2014 and 2018, the number of saltwater recreational fishing trips made by charter boats for hire was fewer from 2019 to 2022.
- An average of 23,815 fishing trips were recorded from 2014 to 2018 (Fig/ 1).
- The total number fell to 20,203 fishing trips in 2019 and 8,984 in 2020 (Fig. 1).
- The total number of fishing trips was still lower at 12,578 in 2021 and 11,757 in 2022 (Fig. 1).
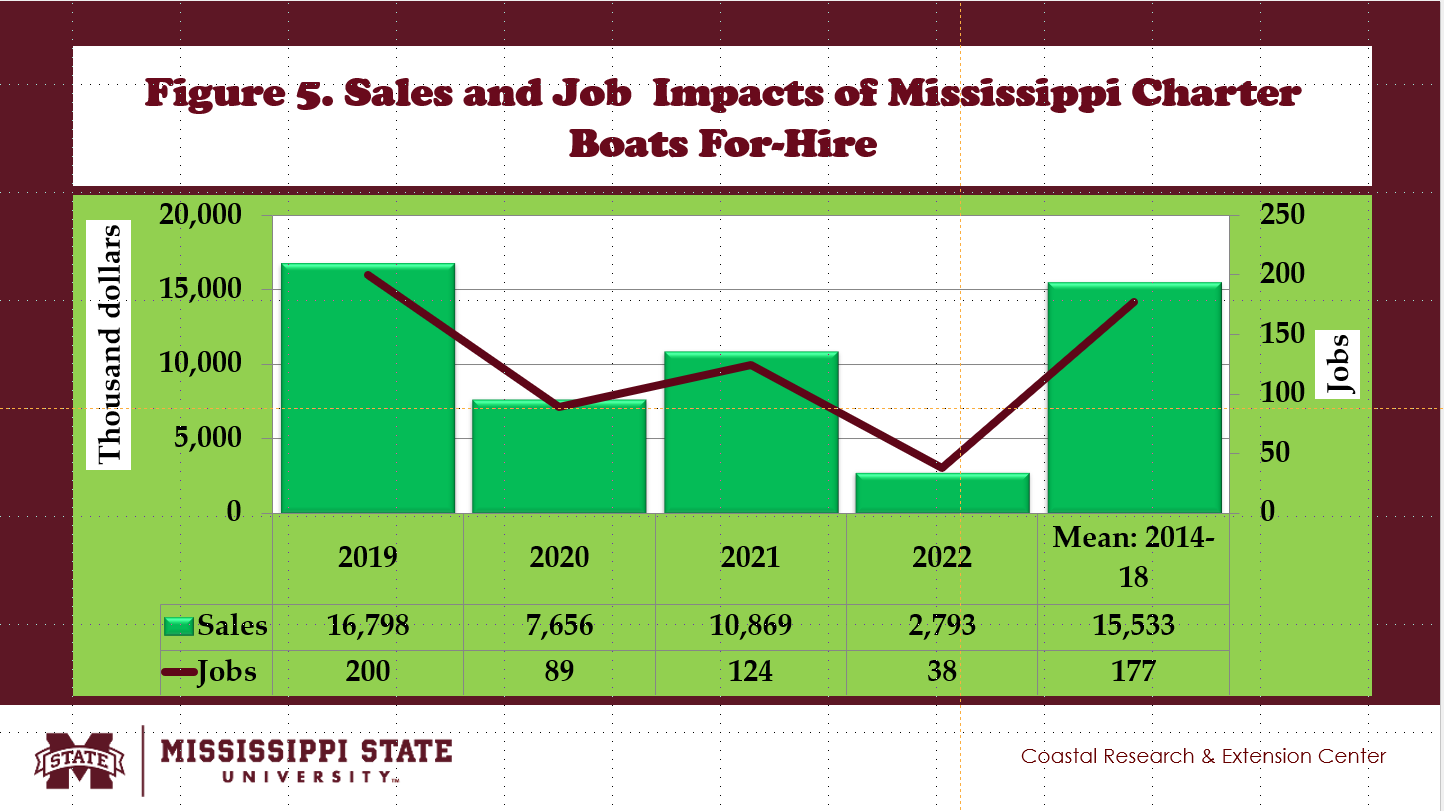
- Fig. 5 shows the annual estimates of the economic impacts of Mississippi charter boats for hire from 2014 to 2022.
- Between 2014 and 2018, the benchmark mean of total sales impacts reached $15.53 million, contributing 0.5% of the U.S. charter boats for-hire industry.
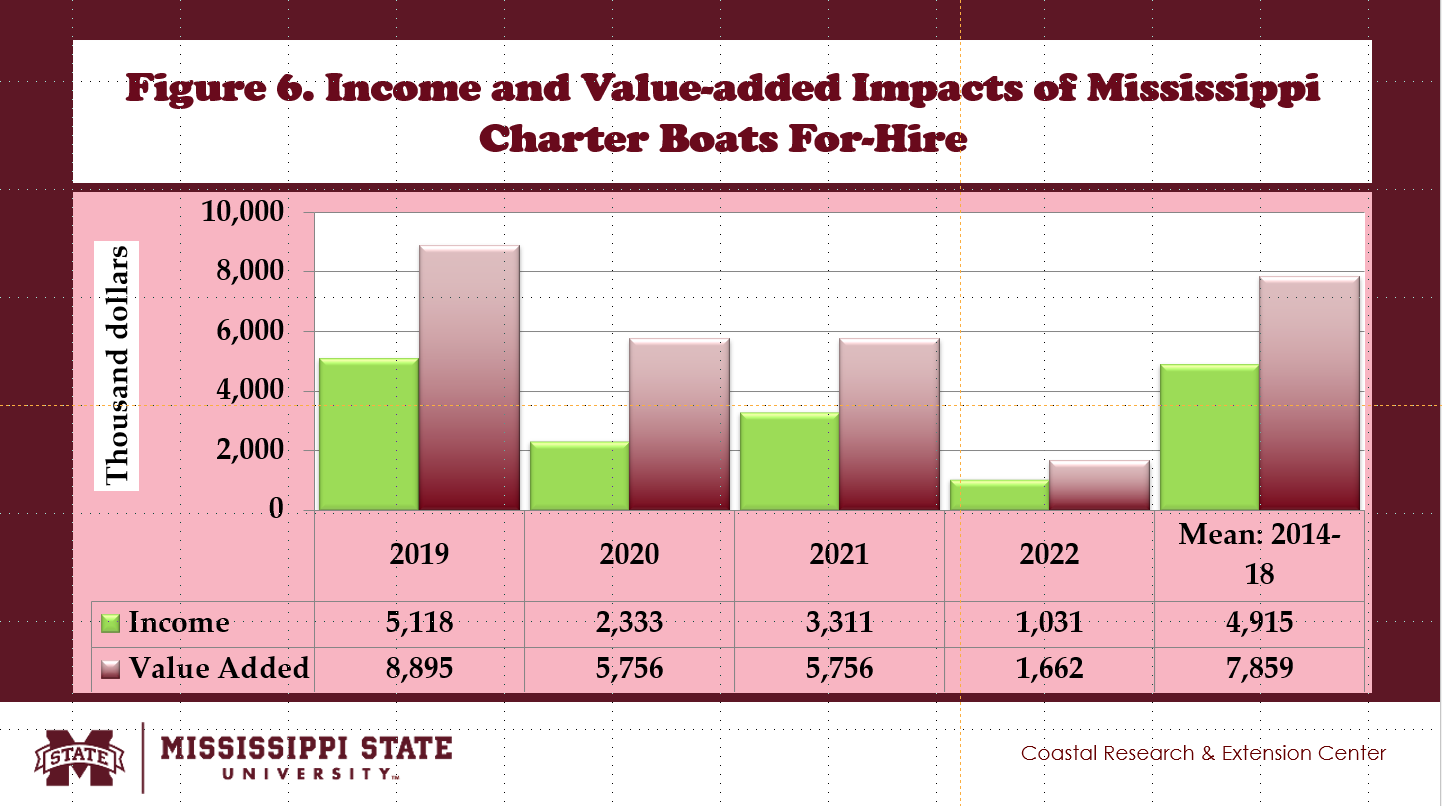
- About 177 jobs were created in Mississippi charter boats for hire, adding 0.8% to the U.S. charter boats for hire industry (Fig. 6).
- Charter boats for hire generated total income impacts in Mississippi, reaching $4.92 million, adding 0.5% to the U.S. charter boats for hire industry (Fig. 6).
- Value-added impacts created by Mississippi charter boats for hire averaged $7.86 million, contributing 0.5% of the U.S. charter boats for hire industry (Fig. 6).
MISSISSIPPI PRIVATE BOAT SALTWATER RECREATIONAL FISHING
- Compared to the mean values between 2014 and 2018, the number of saltwater recreational fishing trips made by private boats was fewer in 2019, 2020, and 2021.
- An average of 1.58 million fishing trips were recorded from 2014 to 2018 (Fig. 1).
- The total number fell to 1.38 million fishing trips in 2019 and 1.45 million in 2020 (Fig. 1).
- The total number of fishing trips was lower at 1.54 million in 2021 and higher at 1.72 million in 2022 (Fig. 1).
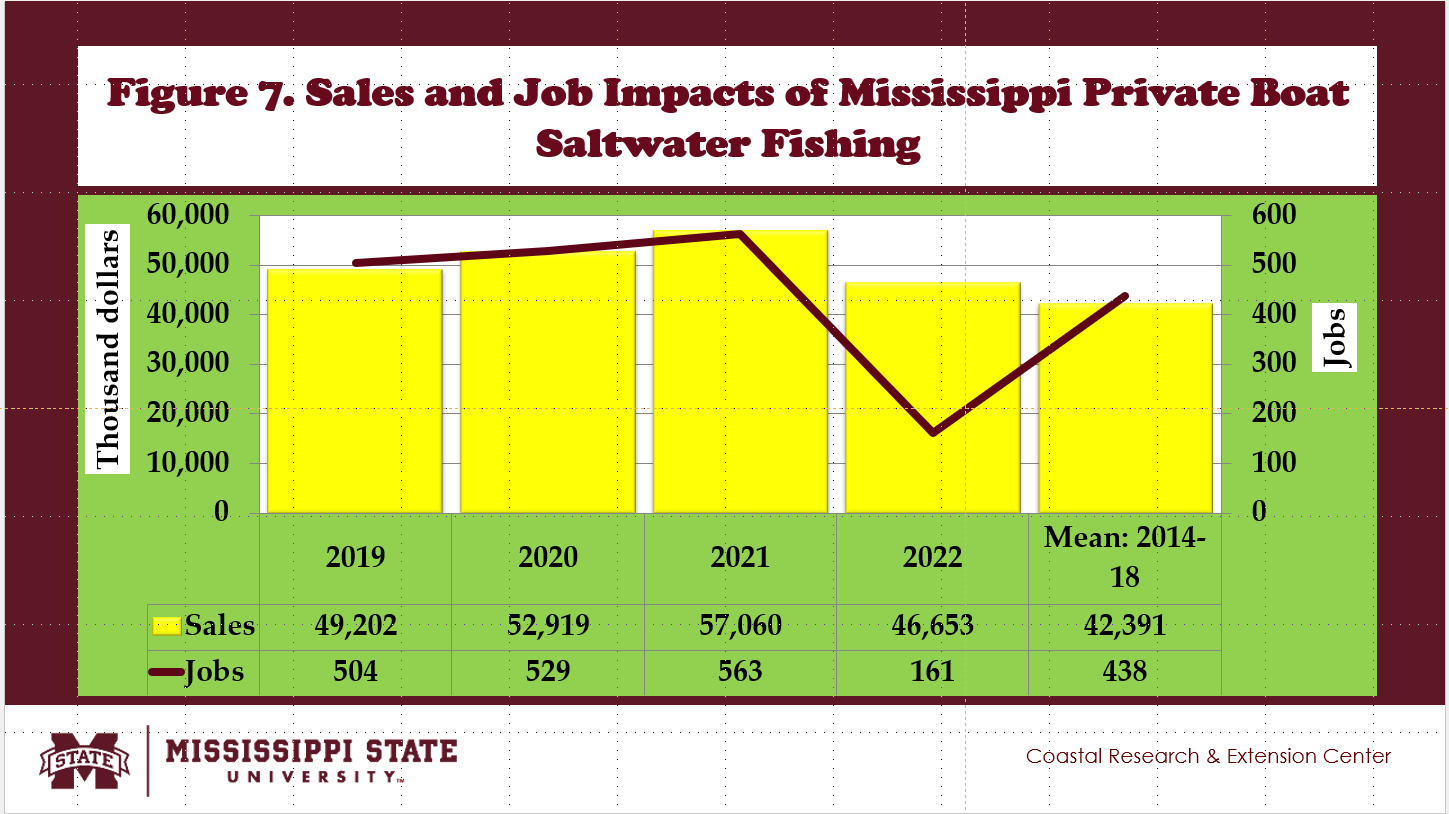
- Fig. 7 shows the annual estimates of the economic impacts of Mississippi private boat saltwater fishing from 2014 to 2022.
- Between 2014 and 2018, the benchmark mean of sales impacts of private boats saltwater fishing reached $42.39 million, contributing 0.6% of the U.S. private boat saltwater fishing industry.
- About 438 jobs were created in Mississippi private boat saltwater fishing, adding 1.2% to the U.S. private boat saltwater fishing industry (Fig. 7).
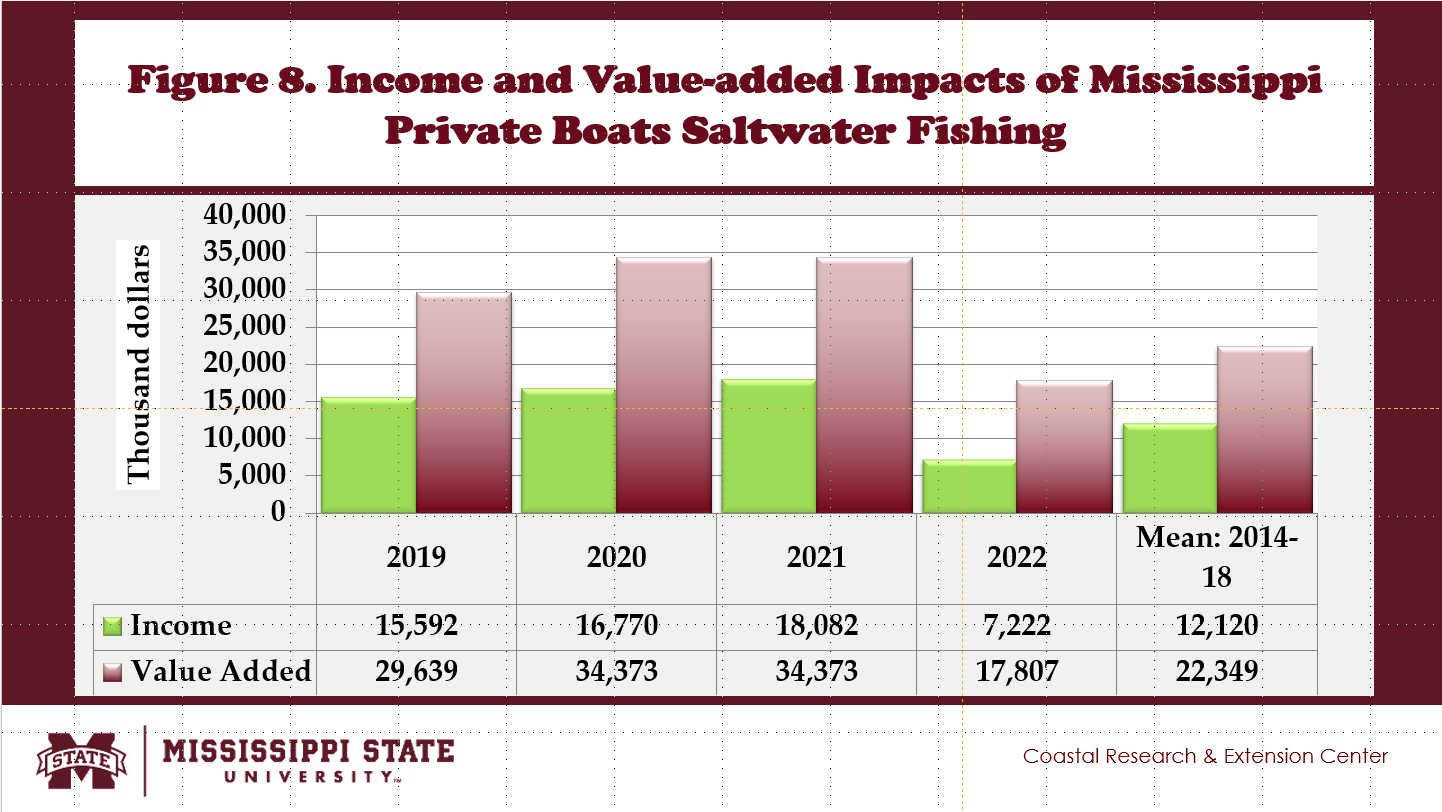
- Private boat saltwater fishing generated income impacts in Mississippi, reaching $12.12 million, adding 0.6% to the U.S. private boat saltwater fishing industry (Fig. 8).
- Value-added impacts created by Mississippi private boats saltwater fishing averaged $22.35 million, contributing 0.7% of the U.S. private boat saltwater fishing industry (Fig. 8).
MISSISSIPPI SALTWATER RECREATIONAL SHORE FISHING
- Compared to the mean values between 2014 and 2018, the number of saltwater recreational fishing trips made by shore fishermen was lesser in 2019, 2020, and 2022.
- An average of 3.00 million fishing trips were recorded from 2014 to 2018 (Fig. 1).
- The total number fell to 2.82 million fishing trips in 2019 and 2.84 million in 2020 (Fig. 1).
- The total number of fishing trips was 3.22 million in 2021 and 2.98 million in 2022 (Fig. 1).
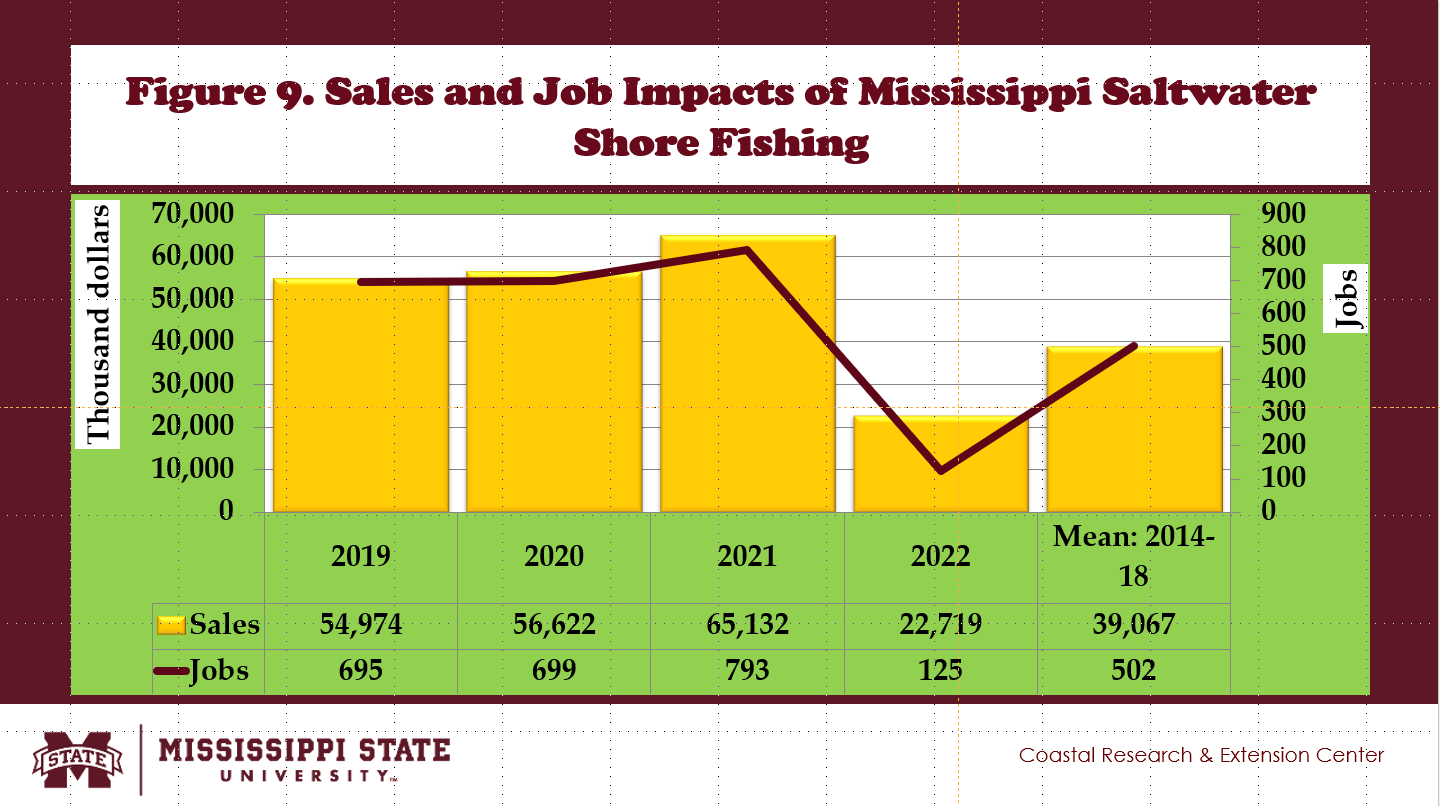
- Fig. 9 shows the annual estimates of the economic impacts of Mississippi saltwater shore fishing from 2014 to 2022.
- Between 2014 and 2018, the benchmark mean of sales impacts of Mississippi saltwater shore fishing reached $39.07 million, contributing 0.5% of the U.S. saltwater shore fishing industry.
- About 502 jobs were created in Mississippi saltwater shore fishing, adding 1.1% to the U.S. saltwater shore fishing industry (Fig. 9).
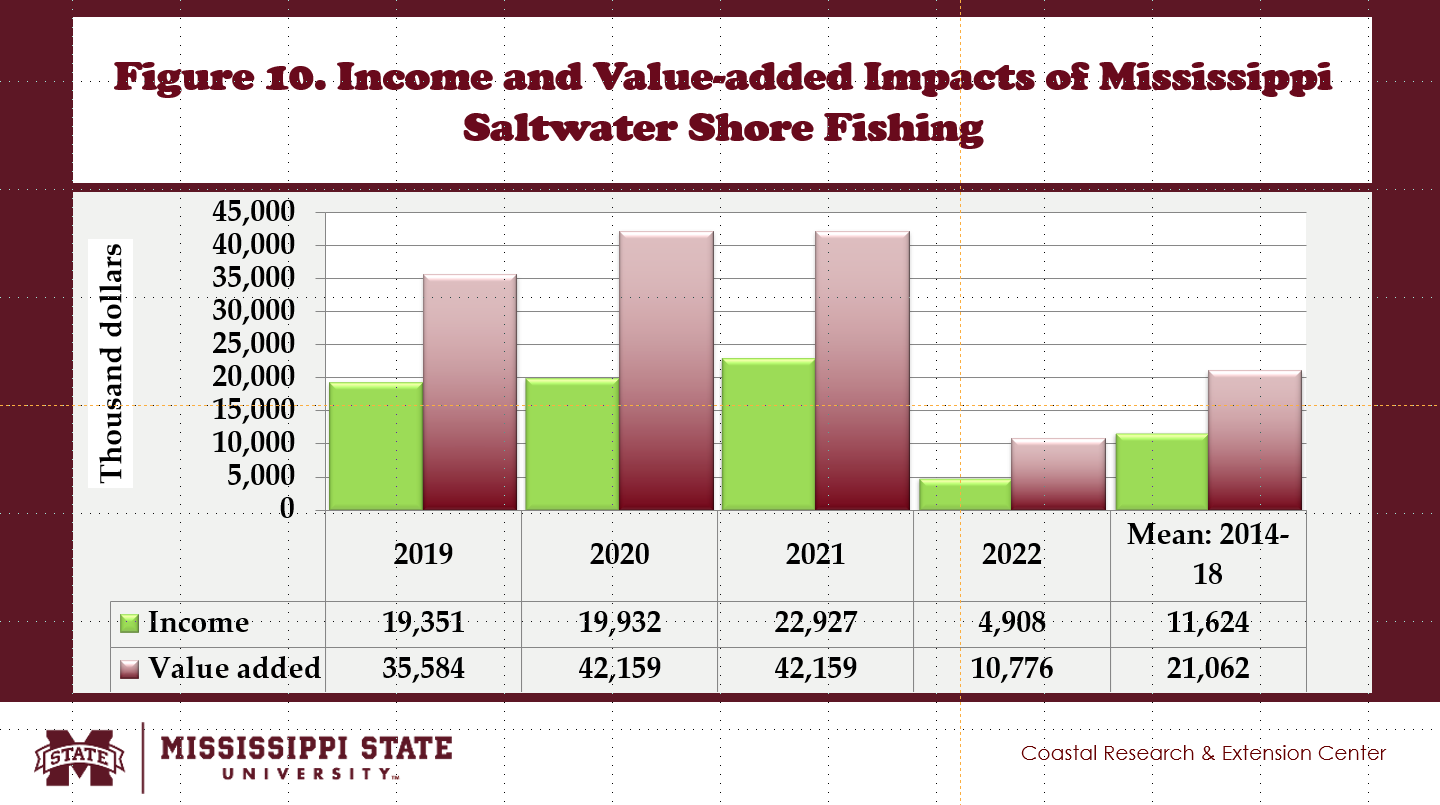
- Saltwater shore fishing generated income impacts in Mississippi, reaching $11.62 million, adding 0.5% to the U.S. saltwater shore fishing industry (Fig. 10).
- Value-added impacts created by Mississippi saltwater shore fishing averaged $21.06 million, contributing 0.6% of the U.S. saltwater shore fishing industry (Fig. 10).
PROFILES OF OWNERS AND WORKERS OF MISSISSIPPI CHARTER BOATS FOR-HIRE
- Annual data from Lightcast (https://analyst.lightcast.io/analyst/, 2024) indicate about 226 Mississippi charter boats for hire owners and workers.
- About 70% are males.
- 86.9% are White, 5.6% are Hispanic, 5.6% are Asians, and 1.86% have two or more races. The rest are Black or African Americans.
- The average age of Mississippi charter boats for-hire owners and workers was 52. About 22% were under 35 years old, -16.7% were between 35 and 54. The 55-year-old and higher owners and workers comprised 61.1%.
SUMMARY, LIMITATIONS, AND IMPLICATIONS
- Total Mississippi saltwater fishing trips decreased by 8% and 7% in 2019 and 2020. No losses in total fishing trips were observed in 2021 and 2022.
- The number of trips made by Mississippi charter boats for hire fell about 15%, 62%, 47%, and 51% in 2019, 2020, 2021, and 2022, respectively.
- The Mississippi private boat saltwater fishing trips decreased by about 13%, 8%, and 3% in 2019, 2020 and 2021.
- The Mississippi saltwater shore fishing trips decreased by 6% and 5% in 2019 and 2020.
- Reduced sales and job impacts were observed among the Mississippi charter boats for hire during the pandemic years.
- This newsletter does not include the economic impacts of durable expenditures on saltwater recreational fishing due to the lack of data.
- Between 2014 and 2018, the Mississippi saltwater recreational fishing industry produced an annual total sales impact of $97 million, 1,117 jobs, a total income impact of $28 million, and value-added impacts of $51 million.
- The Mississippi charter boats for hire generated an annual total sales impact of $15 million, 177 jobs, a total income impact of $5 million, and value-added impacts of $8 million.
- The Mississippi private boat saltwater recreational fishing created an annual total sales impact of $42 million, 438 jobs, a total income impact of $12 million, and value-added impacts of $22 million.
- The Mississippi saltwater recreational shore fishing generated an annual total sales impact of $39 million, 502 jobs, a total income impact of $12 million, and value-added impacts of $21 million.
SUGGESTED CITATION
Posadas, Benedict C. 2024. Economic Impacts of Mississippi Saltwater Recreational Fishing Industry. Mississippi MarkeMaker Newsletter, Vol. 14, No. 10. Mississippi State University Extension and Mississippi-Alabama Sea Grant Publication number MASGP-24-057-10. October 11, 2024. https://extension.msstate.edu/newsletters/mississippi-marketmaker.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This newsletter is a contribution of the Mississippi Agricultural and Forestry Experiment Station and the Mississippi State University Extension Service. This material is based upon work that is supported in part by the National Institute of Food and Agriculture, U.S. Department of Agriculture, Hatch project under accession number 100004, and Mississippi-Alabama Sea Grant Consortium using federal funds under Grant NA24OAR4170090 from the National Sea Grant Office, NOAA, U.S. Dept. of Commerce. The statements, findings, conclusions, and recommendations are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Sea Grant Program, NOAA, U.S. Department of Commerce. This newsletter is a Mississippi-Alabama Sea Grant Publication number MASGP-24-057-10.
For accessibility assistance please contact Ben Posadas at ben.posadas@msstate.edu









