Considerations for Replant Decisions in Soybean
Replant decisions typically fall into one of three categories: (1) keep the crop as is; (2) replant it all; or (3) reduce your seeding rate, and plant into the existing stand. The decisions to keep the stand or to terminate and start over are generally the simplest. Fields with marginal stands that appear to be thin yet uniform often present more difficult decisions. Traditionally, in these situations, a supplemental planting may occur with a reduced seeding rate to bring the total plant population up to the desired level. However, little research has specifically addressed whether the added plants improve soybean yield and profitability.
Research was conducted in Mississippi to evaluate soybean yield at various stands and replanting approaches. The target seeding rate was 130,000 seeds per acre. Several removal and replant treatments were imposed to simulate marginal stands and replant methods commonly used in the field. The treatments listed in Table 1 are expressed as percentage of stand loss relative to the initial planting and replanted density.
Yield results are displayed in Figure 1. When the soybean stand was 50 percent or more of the intended population, replanting into the existing soybean did not improve grain yield compared to maintaining a reduced stand. However, when 75 percent of the initial soybean stand was lost, replanting into the existing stand improved grain yield 12 percent compared with keeping that level of reduced stand as is. This finding suggests that soybean replanting recommendations should vary depending upon the degree of stand failure. Assuming uniformity of the existing soybean, stands reduced less than 50 percent may be maintained without replanting. However, when soybean growers experience a severely reduced stand (75 percent stand loss), the best option is to retain the crop and replant additional seed to supplement the reduced stand. When stand failure is complete or the initial planting is terminated, replanting at a later date will likely reduce soybean yield potential considerably.
Table 1. Replant scenario and population description
|
Existing population description |
Replant treatment |
Percent stand loss from initial planting1 |
Percent of target population to replant2 |
Percent of target population achieved3 |
|
Target population achieved |
None |
0 |
0 |
100 |
|
Some stand loss |
Reduced rate planted into existing stand |
25 |
25 |
100 |
|
Some stand loss |
Keep as is |
25 |
0 |
75 |
|
Moderate stand loss |
Reduced rate planted into existing stand |
50 |
50 |
100 |
|
Moderate stand loss |
Keep as is |
50 |
0 |
50 |
|
Severe stand loss |
Reduced rate planted into existing stand |
75 |
75 |
100 |
|
Severe stand loss |
Keep as is |
75 |
0 |
25 |
|
Terminate failed stand |
Full Replant |
100 |
100 |
100 |
1Percent loss from targeted population following initial planting.
2Percent of targeted population to replant into existing soybean stand.
3Percent of overall targeted population achieved either with initial planting alone or between initial planting and one replant attempt.
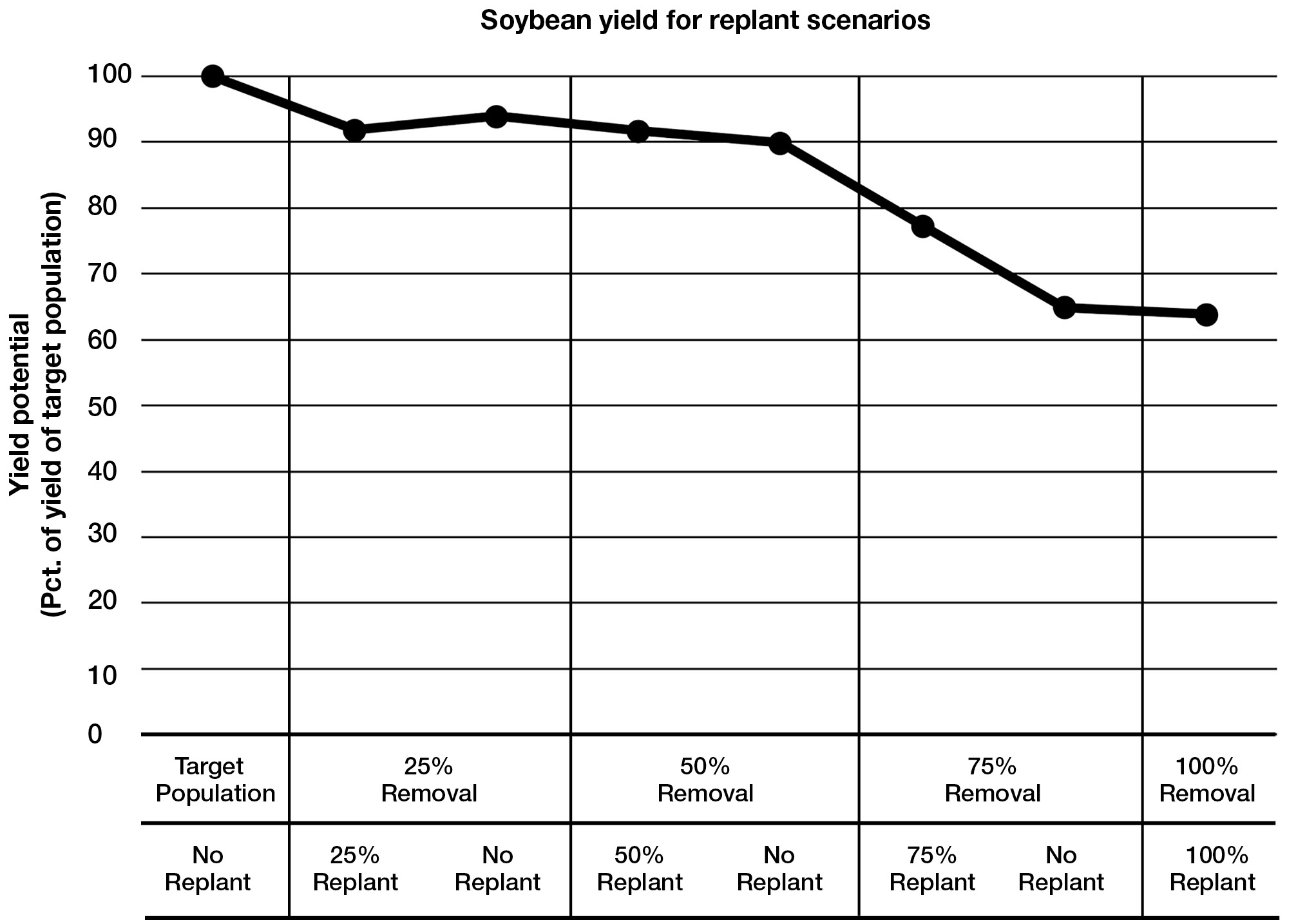
Figure 1. Soybean yield observed across each population removal and replant scenario.
Publication 3831 (POD-10-22)
By Trent Irby, PhD, Associate Extension Professor, and Alanna B. Scholtes, Extension Associate III.
The information given here is for educational purposes only. References to commercial products, trade names, or suppliers are made with the understanding that no endorsement is implied and that no discrimination against other products or suppliers is intended.
The Mississippi State University Extension Service is working to ensure all web content is accessible to all users. If you need assistance accessing any of our content, please email the webteam or call 662-325-2262.



